10 Best Robotic Grinding Solutions for Precision Manufacturing?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, robotic grinding has emerged as a key player. According to a market report by Grand View Research, the global robotic grinding market is projected to reach $12 billion by 2027, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of over 15%. This growth highlights the increasing demand for precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Industry experts, such as Dr. Anna Groß, a leading figure in robotic automation, emphasize the significance of this technology. She once stated, “Robotic grinding represents a paradigm shift in how we approach material removal and finishing processes.” This perspective underlines the importance of integrating advanced robotic systems in achieving superior surface finishes and reducing operational costs.
Despite the advantages, challenges remain. Implementing robotic grinding solutions requires careful planning and investment. Many manufacturers face obstacles in adapting their workflows to incorporate these advanced systems. Without addressing these concerns, the transition could lead to inefficiencies. Understanding both the potential and the pitfalls of robotic grinding is crucial for manufacturers looking to remain competitive in a demanding market.

Top Features to Look for in Robotic Grinding Solutions
In precision manufacturing, selecting the right robotic grinding solution is crucial. Top features to look for include flexibility and adaptability. A system that can handle various materials is invaluable. According to industry reports, about 70% of manufacturers seek versatile solutions to manage different projects. This adaptability often leads to cost savings and efficiency gains.
Another essential feature is precision. Robotic systems must achieve high accuracy, often within microns. Data shows that precise grinding can reduce material waste by nearly 30%. However, many solutions struggle with maintaining consistency over time. Regular calibration and maintenance can enhance performance, yet this aspect is often overlooked.
Speed also plays a significant role. High-speed grinding systems can significantly reduce cycle times. Yet, faster does not always mean better. Operators must assess whether speed compromises quality. A balance between speed and precision is vital. Many companies report challenges in achieving this balance, highlighting the need for continuous improvement in robotic grinding technology.
Best Types of Robots for Precision Grinding in Manufacturing
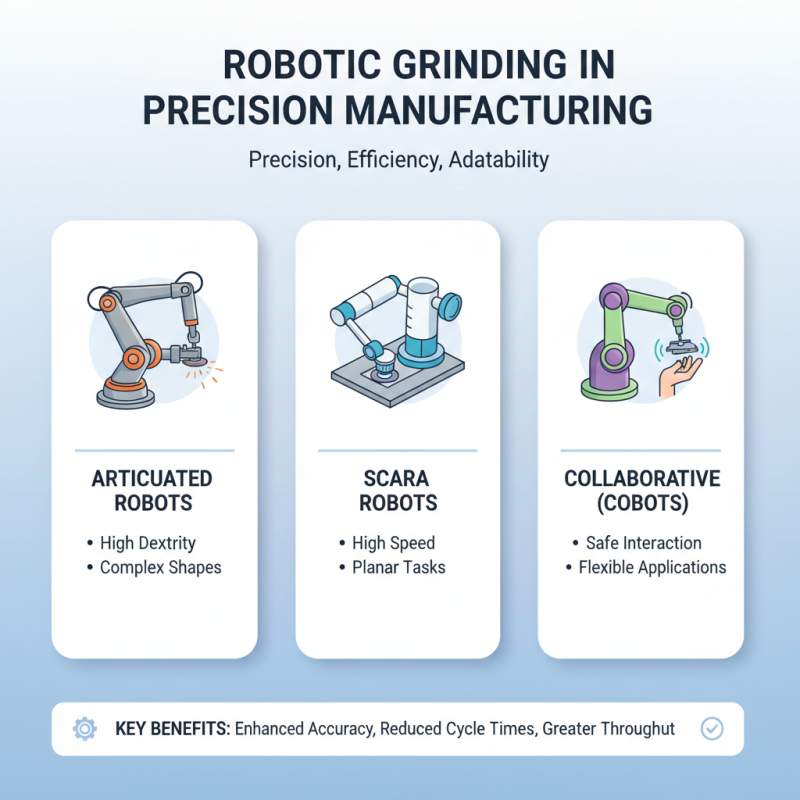
In the world of precision manufacturing, robotic grinding has gained significant traction. Various types of robots excel in this domain, offering precise control and efficiency. The most popular choices include articulated robots, SCARA robots, and collaborative robots. Each type serves unique purposes, adapting to different grinding tasks with ease.
Articulated robots are versatile. They can reach complex geometries and provide high accuracy. A report by the International Federation of Robotics states that articulated robots account for about 50% of all industrial robot sales. However, they can require extensive programming and sometimes struggle with repetitive tasks. SCARA robots, on the other hand, are ideal for high-speed applications and are often easier to program. Their rigid structure allows for quick and precise movements.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, offer a more flexible solution. They can work alongside human operators, enhancing safety while maintaining productivity. According to a recent study, cobots can increase manufacturing efficiency by up to 30%. Nevertheless, they still require careful calibration and oversight to ensure they complement human workflow effectively. Adopting the right robot is crucial. Each type has strengths and challenges that must be considered for optimal performance.
Key Benefits of Implementing Robotic Grinding Systems
Robotic grinding systems offer significant advantages for precision manufacturing. One key benefit is enhanced accuracy. Reports indicate that robotic systems can achieve tolerances of ±0.1 mm. This precision is crucial for industries that require exact specifications, such as aerospace and automotive. By adopting robotic grinding, manufacturers can reduce defects and waste. A decrease in rework rates can save costs and time.
Additionally, implementing robotic grinding solutions improves productivity. Data suggests these systems can operate up to 24 hours a day, unlike human workers who need breaks. This continuous operation can lead to a 30% increase in output. However, the initial setup cost may be a barrier for some companies. Organizations often struggle with integrating these systems into existing workflows. Issues like training staff and maintaining equipment are common concerns.
Moreover, robotic grinding can ensure consistent quality. Robots perform repetitive tasks with minimal variation, while human work can be inconsistent. However, this high level of automation might create challenges. Some operators may feel disconnected from the production process. Over-reliance on automation can lead to skill degradation among workers. Balancing automation with human expertise is essential for sustainable practices.
Leading Robotic Grinding Technologies Transforming the Industry
Robotic grinding technologies are revolutionizing precision manufacturing. These advanced systems offer personalized automation solutions. According to a recent industry report, the global robotic grinding market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth signals a strong demand for efficient and precise manufacturing processes.
Many manufacturers are adopting robotic grinding to improve product quality and reduce labor costs. Studies show that robotic systems can enhance grinding accuracy by up to 30%. However, integrating these technologies can pose challenges. Companies often face steep learning curves and high initial investment costs. Additionally, consistent maintenance of robotic systems is crucial for optimal performance.
The adoption of robotic grinding also raises questions about workforce displacement. While automation boosts production efficiency, it may reduce job opportunities. Striking a balance between technology and human skills remains essential. As industries transition, reflections on ethical implications and workforce training become vital. The future of robotic grinding must consider not just productivity, but also human impact.
10 Best Robotic Grinding Solutions for Precision Manufacturing
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Robotic Grinding Solutions
Robotic grinding solutions have gained traction in precision manufacturing. Many industries report time and cost savings of 30% to 50%. Case studies highlight diverse applications, from automotive parts to aerospace components. For instance, one manufacturer automated the grinding of turbine blades, significantly enhancing surface finish and reducing cycle time.
Implementing robotic grinding can involve challenges. Operators need to ensure proper programming and calibration. A learning curve may exist when integrating new technology. However, successful cases show that overcoming initial hurdles pays off. A study revealed that automation can improve consistency in output, minimizing rework and scrap rates.
Tip: Invest time in training your team. Knowledge of programming and maintenance is crucial for long-term success. Regularly reviewing processes can identify areas for improvement. Engage in continuous learning to stay updated with industry advancements. Embracing the robotic revolution may yield substantial benefits, but adaptability is key.
Related Posts
-

5 Essential Tips for Optimizing Robotic Grinding Efficiency: Boost Your Production by 30%
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Impact of Automated Welding Cells on Production Efficiency
-

2025 Top 5 Robotic Systems Transforming Industries with 50% Efficiency Boost
-

Top 10 Robotic Welding Classes to Enhance Your Skills in 2023
-

2025 Top 5 Robotic Welding Classes for Advanced Skills and Career Growth
-
How to Choose the Best Robot Automation Software for Your Business?
